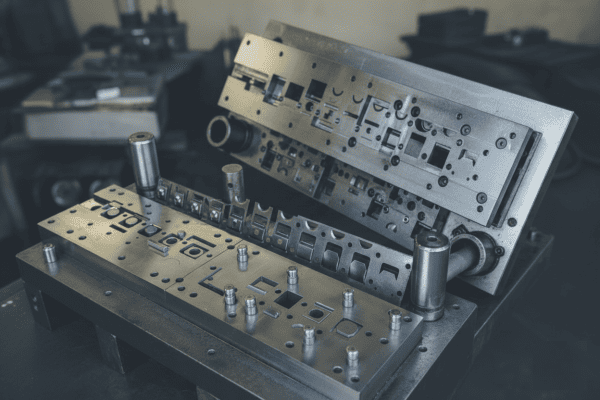
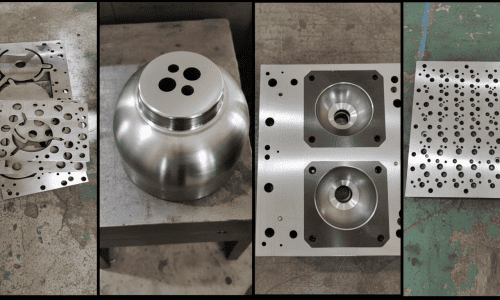
Progressive
Die Stamping
Solutions
Multiple operations in one press cycle--ideal for terminals, brackets, and complex stamped parts.
Understanding Multi-Stage Metal Forming
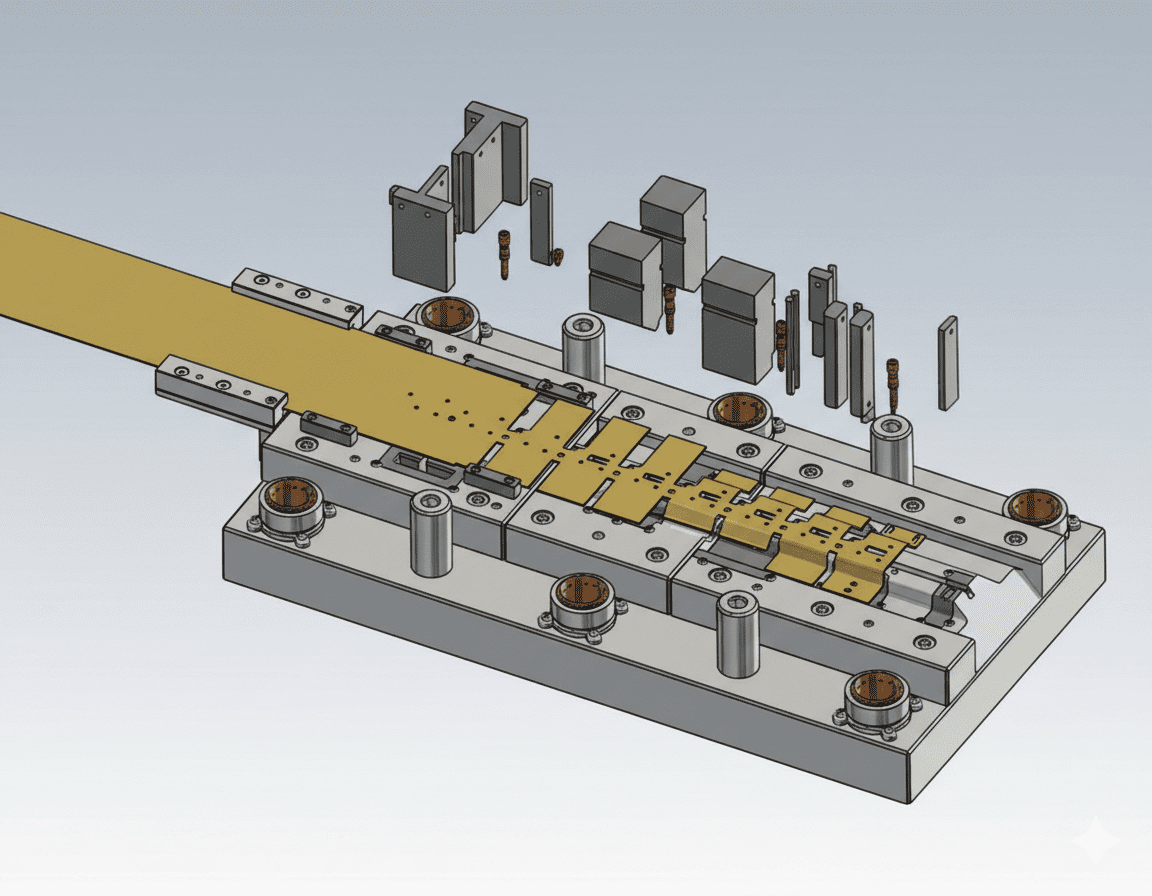
Definition: Progressive die stamping is a continuous feeding process where coil or strip material advances through multiple stations, sequentially performing operations like punching, blanking, bending, forming, and cutting in a single press cycle.
Core Value: Delivers consistent cycle times, exceptional dimensional accuracy, and dramatically reduced unit costs at high volumes. The automated process ensures repeatable quality while minimizing material waste and labor requirements.
Applications: Ideal for manufacturing electrical terminals, connectors, spring contacts, mounting brackets, EMI/RFI shielding cases, and other high-precision metal components requiring millions of identical parts.
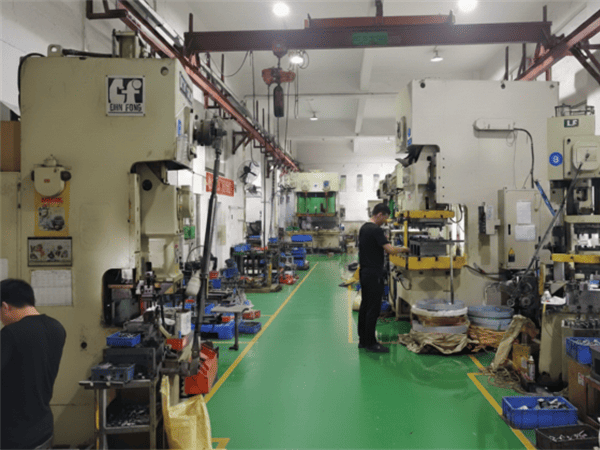
Advanced Stamping Capabilities
State-of-the-art equipment and expert engineering for complex progressive die stamping projects.
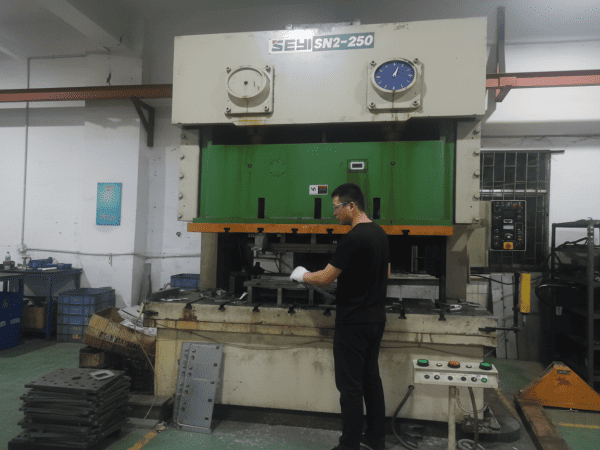
Technical Specifications
| Press Tonnage | 25-250T |
| Material Thickness | 0.5-6.0mm |
| Tolerance | ±0.01-±0.05mm |
| Supported Operations |
Piercing
Blanking
Bending
Forming
Coining
Cut-off
|
| Secondary Operations |
|
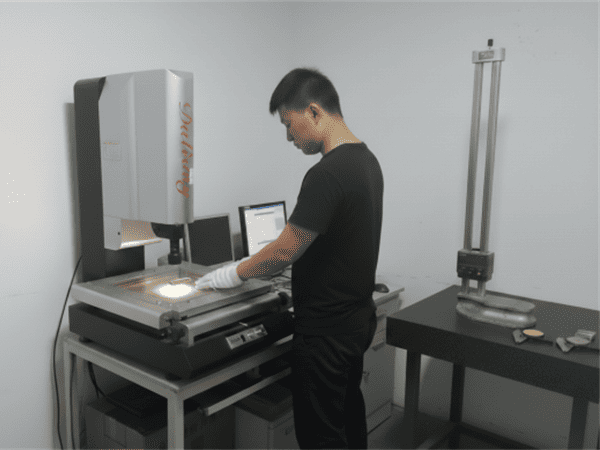
| Inspection |
FAI
Dimensional Report
CMM
|
From Design to Production
Our comprehensive approach ensures optimal die design and flawless production setup.
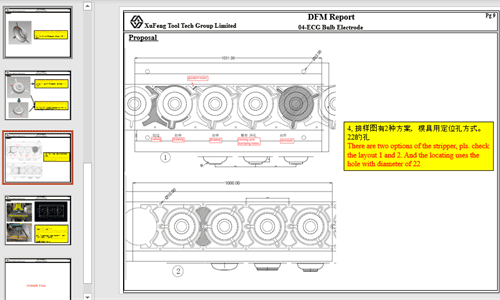
Design Analysis & DFM
- Feasibility study
- Strip layout optimization
- Material utilization analysis
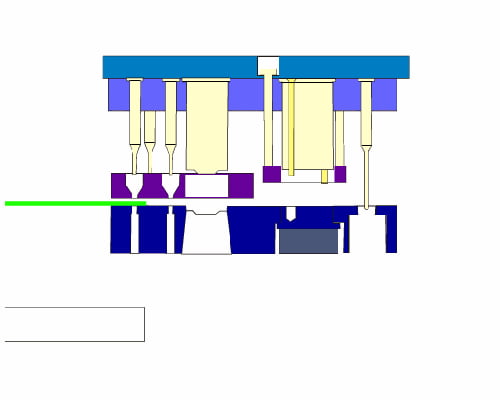
Die Design & Simulation
- 3D die modeling
- Forming simulation
- Spring-back compensation
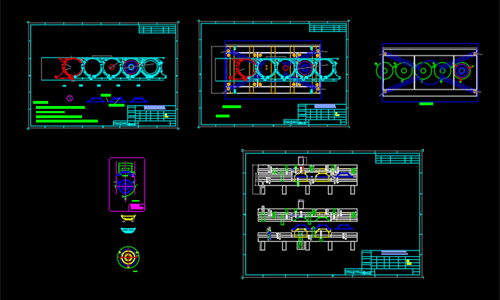
Die Manufacturing & Assembly
- CNC machining
- Heat treatment
- Surface coating
Tryout & Optimization
- First article inspection
- Die adjustments
- Process validation
Understanding Progressive Die Stamping
Make informed decisions with a clear understanding of the benefits and constraints of progressive die stamping.
Key Advantages
High Production Speed
Up to 800 strokes per minute for maximum throughput and reduced per-piece costs.
Excellent Repeatability
Consistent dimensional accuracy across millions of parts with minimal variation.
Complex Geometries
Multiple operations in one pass: punching, bending, coining, and forming.
Material Efficiency
Optimized strip layout minimizes waste and reduces material costs.
Reduced Labor Costs
Automated operation requires minimal operator intervention once setup.
Superior Surface Finish
Cold forming process produces excellent surface quality without secondary operations.
Considerations
High Initial Investment
Die design and manufacturing costs require high-volume production to justify.
Design Constraints
Part geometry must be suitable for progressive forming operations.
Material Limitations
Some materials may not be suitable for cold forming or progressive operations.
Setup Complexity
Initial die setup and optimization can be time-consuming and requires expertise.
Size Limitations
Press bed size and tonnage capacity limit maximum part dimensions.
Design Changes
Modifications to existing dies can be costly and time-consuming.
When is Progressive Die Stamping Right for You?
Progressive die stamping becomes cost-effective when production volumes exceed 50,000-100,000 pieces annually, depending on part complexity.
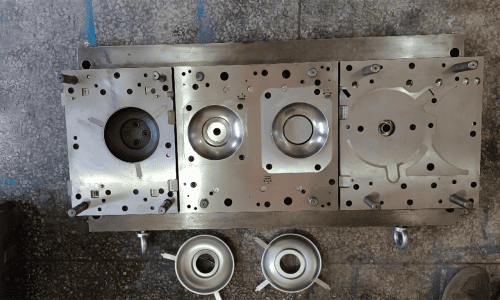
Success Story: Water heater gas cap
How we helped a major automotive supplier reduce costs by 45% while improving quality and delivery times.
Project Overview
Challenge
1-meter press table for 9 steps progressive die. Seeking a supplier capable of transforming a simple hand sketch into a fully functional progressive die.
Solution
We designed a 9-station progressive die and combined selected operations into shared stations to fit the customer’s 1-meter press bed. During the design phase, we also optimized material utilization to minimize scrap, controlled the cut-off/punching loads, and mitigated the risk of drawing splits/tearing. As a result, the process was streamlined without sacrificing dimensional tolerances, while ensuring smooth blanking and reliable part ejection/strip progression.
Read the full caseImpressive Results
Process Comparison

Metal Stamping Knowledge Base
Master the fundamentals of progressive die stamping with our comprehensive technical guides and industry best practices.
How to Choose: Progressive vs Transfer vs Compound Stamping
Compare three major stamping methods to select the optimal approach for your part complexity, volume requirements, and cost targets.
- Production volume analysis
- Part complexity considerations
- Cost-benefit comparison
Progressive Die DFM: Key Design Rules for Cost & Stability
Essential Design for Manufacturing guidelines to optimize your parts for progressive die stamping efficiency and quality.
- Strip layout optimization
- Feature spacing rules
- Material flow considerations
Stamping Quality 101: Tolerance, Burr Control & Inspection
Master quality control fundamentals including tolerance management, burr reduction techniques, and inspection protocols.
- Tolerance stack-up analysis
- Burr formation prevention
- Statistical process control
Need Expert Advice on Your
Stamping Project?
Our engineering team provides free DFM analysis and technical consultation to optimize your parts for progressive die stamping success.